By Carolina Herrera
Vaping is safer than smoking tobacco you say? Tobacco smoking in the U.S. has decreased, however due to this decline, tobacco companies have promoted electronic cigarettes (e-cigs) as safer alternatives to tobacco cigarettes. E-cigs are battery-operated devices that produce aerosols by heating up nicotine, flavorings and other components. However, what people don’t know is that flavored e-cig liquids and e-cig aerosols contain airway toxicants and irritants that have been associated with the worsening of lung diseases. E-cig aerosols can contain cancer-causing chemicals and heavy metals, such as nickel, tin, and lead. E-cigs debuted in the U.S. in 2007 and have especially gained popularity among teenagers and young adults.The main components of e-cigs are propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin, nicotine, and e-liquid flavorings.
There are over 7,000 e-cig liquids which contain flavorings that have not been evaluated for inhalation toxicity by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). While the FDA has classified many of these flavorings as generally recognized as safe (GRAS) for oral consumption, continued inhalation of some GRAS flavorings can lead to irreversible lung damage. The health risks of vaping are greater than originally thought and the number of vaping-related illnesses and deaths in the U.S. is on the rise.
Vaping poses a threat to your immune system. The human respiratory tract is susceptible to pollutants and pathogens, such as viruses and bacteria because we breathe in approximately 12,000 liters of air per day! Lung epithelial cells are the first line of defense against all pollutants and pathogens that you may inhale. In addition, your immune system is a system of cells, tissues, and organs that protects your body from infection and disease and there are many immune cells in your respiratory tract. Immune cells such as neutrophils and macrophages respond to pathogens in the lung/respiratory tract. Neutrophils and macrophages can phagocytose, or chew up, invading pathogens and produce toxic enzymes that kill pathogens. The proper function of these immune cells is crucial to helping protect your body from infection. However, vaping can impair the ability of lung epithelial cells and your immune system cells to function properly.
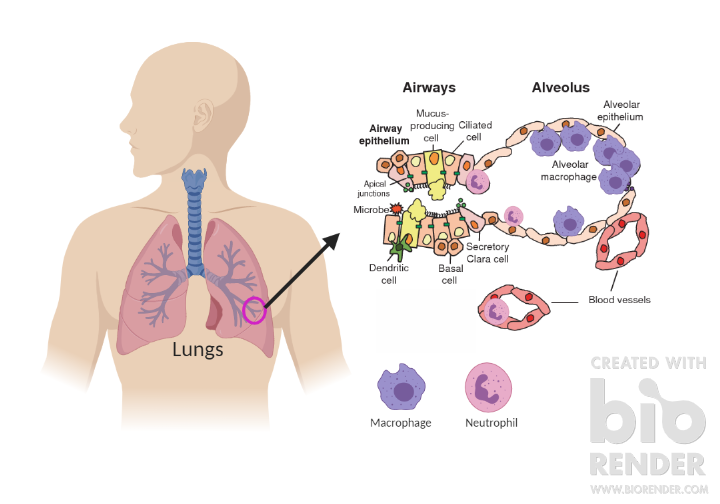 Every day, scientists are understanding more about the harmful effects of e-cigs on the immune system. Scientists at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill demonstrated that flavored e-cig liquids, such as cinnamaldehyde (cinnamon flavored e-liquids) can impair the ability of neutrophils to phagocytose foreign pathogens, such as bacteria. Scientists at Johns Hopkins have shown that mice who were exposed to e-cig vapor for two weeks and then exposed to Influenza A (flu virus) had infections that were much more severe compared to mice who were only exposed to Influenza A. Furthermore, another study showed that e-cig vapor affects the function of lung epithelial cells by affecting the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) in lung epithelial cells, which is important in the transport and clearance of mucus in your lungs.
Every day, scientists are understanding more about the harmful effects of e-cigs on the immune system. Scientists at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill demonstrated that flavored e-cig liquids, such as cinnamaldehyde (cinnamon flavored e-liquids) can impair the ability of neutrophils to phagocytose foreign pathogens, such as bacteria. Scientists at Johns Hopkins have shown that mice who were exposed to e-cig vapor for two weeks and then exposed to Influenza A (flu virus) had infections that were much more severe compared to mice who were only exposed to Influenza A. Furthermore, another study showed that e-cig vapor affects the function of lung epithelial cells by affecting the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) in lung epithelial cells, which is important in the transport and clearance of mucus in your lungs.
Overall, these studies and numerous others have shown that e-cig liquids and e-cig vapor can impair lung cell and immune cell responses. These effects can increase the susceptibility to infection and the worsening of respiratory diseases. Since so many e-cigarette liquids are not regulated by the FDA, scientists are working hard to unravel the toxicity of e-cigarettes. Stay tuned!
Edited by Jenna Beam and Rachel Cherney

